About
The Internet of Things (IoT) is growing rapidly. IoT is the connectivity of devices over the internet. It’s like a social network or an email service, but instead of connecting people, IoT actually connects smart devices which include, but not limited to your computers, smartphones, smart home appliances, automation tools, and more.
However, similar to all types of technologies out there, IoT is a double-edged sword as well. It has its upsides, but there are serious threats that accompany this technology. As manufacturers are racing against each other to bring the latest device in the market, not many of them are thinking about the security issues associated with their IoT devices.
Most Common IoT Security Threats
What are the biggest security threats and challenges that IoT faces right now? This question is one of the most asked queries by various user groups as they are the end-users. Basically, there are many IoT security threats that prevail in our day to day used IoT devices which make this tech world more vulnerable.
To keep our IoT system out of security holes, we have to identify and solve the threats and challenges. Here, I have made a small endeavor to identify a list of most common IoT security threats that will help us to take the suitable safeguards.
1. Lack of Updates
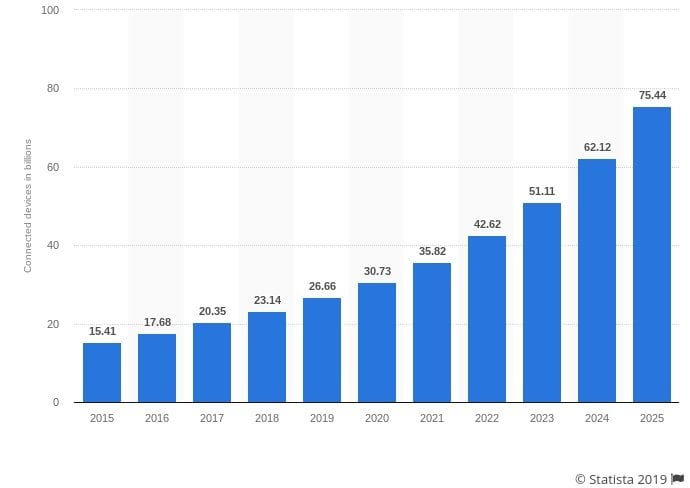
Right now, there are around 23 billion IoT devices around the world. By 2020, this number will rise to nearly 30 billion, says Statista report. This massive boost in the number of IoT connected devices doesn’t come without any consequences.
The biggest problem with all the companies that are churning out these devices is that they are careless in terms of handling device-related security issues and risks. Most of these connected devices don’t get enough security updates; some never get updated at all.
Devices that were once thought to be secure become completely vulnerable and insecure with the evolution of technology, making them prone to cybercriminals and hackers.
Manufacturers are competing with each other and releasing devices every day without thinking much about the security risks and issues.
Most manufacturers do provide Over-the-air (OTA) firmware updates, but these updates stop as soon as they start working on their new device, leaving their current generation exposed to attacks.
If the companies fail to provide security updates for their devices regularly, then they are exposing their customer base to potential cyber-attacks and data breaches.
2. Compromised IoT Devices Sending Spam Emails
The evolution of technology has brought us a plethora of smart devices which include, but not limited to smart appliances, smart home system, etc. These devices use similar computing power as other IoT connected devices and can be used for various activities.

A compromised device can be turned into an email server. According to a report by the Internet security firm Proofpoint, a smart refrigerator was used to send thousands of spam emails without its owners having any clue. Most of these smart devices are capable of being turned into email servers for the purpose of sending mass email spam.
3. IoT Devices Conscripted into Botnets
Similar to devices being hijacked and turned into email servers for mass spam; smart IoT devices can also be used as botnets for conducting DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks.

In the past, hackers have used baby monitors, webcams, streaming boxes, printers, and even smartwatches to carry out large scale DDoS attacks. Manufacturers need to understand the risks associated with IoT connected devices and take all the necessary steps to secure their devices.
4. Unsafe Communication
Many IoT devices don’t encrypt the messages when sending them over the network. This is one of the biggest IoT security challenges out there. Companies need to ensure that communication between devices and cloud services is secure and encrypted.
The best practice to ensure secure communication is to use transport encryption and to use standards like TLS. Isolating devices through the use of different networks also helps create secure and private communication, which keeps the transmitted data secure and confidential. Most apps and services have begun encrypting their messages in order to keep their users’ information secure.
5. Use of Default Passwords
Most companies ship devices with default passwords and don’t even tell their customers to change them. This is one of the biggest IoT security threats as the default passwords are common knowledge, and criminals can easily get their hands on the passwords for brute-forcing.

Weak credentials leave almost all the IoT connected devices prone to brute-forcing and password hacking. Companies using unsafe credentials on their IoT devices are putting both their customers and their business at risk of being susceptible to direct attacks and being infected through a brute-force attempt.
6. Remote Access
Documents released by WikiLeaks mentioned that the Central Intelligence Agency of the United States (CIA) had been hacking into IoT devices and turning the camera/microphones on without the knowledge of the owners. Well, the possibility that attackers can get inside your devices and record the owners without their knowledge is terrifying, and it was used by none other than the Government itself.
Their documents pointed to massive vulnerabilities in the latest software such as Android and iOS, which means criminals can also take advantage of these vulnerabilities and carry out outrageous crimes.
7. Personal Information Leaks
Experienced cybercriminals can cause massive damage even by finding out internet protocol (IP) addresses through unsecured IoT devices. These addresses can be used to pinpoint a user’s location and their actual residential address.

This is why many internet security experts recommend securing your IoT connection through a virtual private network (VPN). Installing a VPN on your router will encrypt all traffic through the ISP. VPN can keep your internet protocol address private and secure your entire home network.
8. Home Invasions
This has to be one of the scariest “Internet of Things security” threats since it bridges the gap between the digital and physical world. As already mentioned, an unsecured IoT device can leak your IP address which can be used to pinpoint your residential address.
Hackers can sell this information to underground websites where criminal outfits operate. Also, if you are using IoT connected smart home security systems, then those could be compromised as well. This is why you need to secure your connected devices through IoT security and the use of VPNs.
9. Remote Vehicle Access
Not as scary as someone breaking into your home, but still something quite terrifying. Today, when we are all yearning for smart driving cars, there’s also a high level of risk associated with these IoT connected cars.
Skilled hackers might get access to your smart car and hijack it through remote access. This is one scary thought because someone else taking control over your car would leave you vulnerable to a plethora of crimes.
Fortunately, smart car manufacturers are paying close attention to these “Internet of Things security” threats and working hard to secure their devices from any kind of breach.
10. Ransomware
Ransomware has been used on PC and corporate networks for a long time. Criminals encrypt your entire system and threaten to remove all your data unless you pay the “Ransom,” thus the name.

It’s only a matter of time before attackers start locking up different smart devices and demanding ransom for their unlocking. Researchers already found out a way to install ransomware on smart thermostats which is quite alarming as criminals can raise or lower the temperature until the ransom has been paid. Even more terrifying is attackers gaining control of home security systems, or smart appliances. How much would you pay to unlock your IoT connected garage door?
11. Data Theft
Hackers are always after data which includes, but not limited to, customer names, customer addresses, credit card numbers, financial details, and more. Even when a corporation has tight IoT security, there are different attack vectors that the cybercriminals can exploit.

For example, one vulnerable IoT device is enough to cripple an entire network and gain access to sensitive information. If such a device is connected to a corporate network, hackers can gain access to the network and extract all the valuable data. The hackers then misuse this data, or sold to other criminals for a large sum.
12. Compromising Medical Devices
This one’s right out of Hollywood, but that doesn’t make it any less of an IoT security threat. An episode of Homeland TV-series showed an attack where the criminals targeted an implanted medical device to assassinate a person.
Now, this type of attack hasn’t been carried out in real life, but it’s still a threat. A threat enough that former Vice President of United States Dick Cheney had the wireless features of his implanted defibrillator removed to avoid such scenarios. As more and more medical devices become connected to IoT, these types of attacks remain a possibility.
13. More Devices, More Threats
This is a downside of having a massive boost in IoT devices. The number of devices behind your firewall has significantly grown in the last decade. Back in the day, we only had to worry about securing our personal computers from outside attacks.
Now, in this age, we have a plethora of different IoT devices to worry about. Ranging from our daily smartphones to smart home appliances and much more. Since there are so many devices that can be hacked, the hackers will always be on the lookout for the weakest link and breach it.
14. Small IoT Attacks
We always find out about large scale IoT attacks. We heard about the Mirai botnet 2 years ago/ Before Mirai; there was Reaper which was much more dangerous than Mirai. Even though large scale attacks cause more damage, we should also be fearing small-scale attacks that often go undetected.
Small-scale attacks often evade detection and slip through the breaches. Hackers will be trying to use these micro attacks to carry out their plans instead of going for the big guns.
15. Automation and A.I
A.I. tools are already being used in the world. There are A.I. tools helping manufacture cars while others are sifting through a large amount of data. However, there’s a downside to using automation since it takes only a single mistake in the code or a faulty algorithm to bring down the entire A.I. network and along with it, the entire infrastructure it was controlling.

A.I. and automation is just code; if somebody gets access to this code, they can take control over the automation and carry out whatever they want. So, we have to ensure that our tools stay safe against such attacks and threats.
16. Human Factor
Well, it’s not an outright threat, but there’s a need to worry about the growing number of devices. Since with each device, the number of humans interacting with IoT also increases. Not everybody is concerned about cybersecurity; some don’t even know anything about digital attacks or consider it a myth.
Such people often have the lowest security standards when it comes to securing their IoT devices. These individuals and their unsecured devices can spell doom for an organization or a corporate network shall they connect to it.
17. Lack of Knowledge
This is also another threat that can be easily solved through the proper sharing of knowledge. People either don’t know much about the IoT or don’t care. The lack of knowledge can often be the cause of massive damage to a corporate or personal network.
It should be prioritized to provide all the fundamental knowledge regarding IoT, connected devices, and the threats to every individual. Having basic knowledge about the impact of IoT and its security threats could be the difference between having a safe network and a data breach.
18. Lack of Time/Money
Most people or organizations won’t invest in a secure IoT infrastructure because they find it too time-consuming or too expensive. This has to change. Otherwise, corporations will face massive financial losses through an attack.
Data is the most valuable asset any corporation can have. A data breach means a loss of millions of dollars. Investing in a secure IoT setup wouldn’t be as costly as a massive data breach.
19. Machine Phishing
Machine phishing will become a significant concern in the coming years. Hackers will infiltrate IoT devices and networks to send fake signals that will cause the owners to take actions that could damage the operational network.

Attackers, for example, could have a manufacturing plant report it’s working on half capacity (while it’s working on 100%) and the plant operator will try to increase further the load which can be devastating for the plant.
20. Poor Authentication Protocols
With so many IoT connected devices flooding the market, the manufacturers have overlooked the fact that each device needs a proper and strong authentication protocol. Such poor authorization mechanisms often lead to providing users with higher access then they are supposed to get.
Most devices lack password complexity, poor default credentials, lack of encryption, no Two-factor authentication, and insecure password recovery. These security vulnerabilities can easily lead to hackers getting easy access to devices and networks.
21. Privacy Concerns
Most devices collect data of all types, which includes sensitive information. Privacy concerns are raised when devices start collecting personal information without having any proper protection methods for that data.
Nowadays, almost all smartphone apps require some type of permissions and data collection on both iOS and Android. You need to review these permissions and see what kind of data is being collected by these apps. If the data collected is of personal and sensitive nature, then it’s better to get rid of the app rather than risk your personal data.
22. Poor Physical Security
Now, we’ve been talking about digital security so far, but that’s not the only threat to an IoT device. If physical security is poor, then hackers can get easy access to the devices without having to do much work.
Physical weaknesses are when a hacker can easily disassemble a device and access its storage. Even having exposed USB ports or other types of ports can lead to hackers gaining access to the device’s storage medium and compromising any data on the device.
23. RFID Skimming
This is the type of skimming where hackers intercept the wireless information and data from RFID chips used on debit cards, credit cards, ID cards/passports, and other documents.

The purpose of skimming this data is to steal the personal information which is used for advanced identity theft. Hackers use NFC-supported devices that record all the unencrypted data from the RFID chips and then broadcast through wireless signals.
24. Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
This is a type of attack where hackers intercept the communication between two parties through an insecure IoT device or a vulnerability in the network, and then they alter the messages while both parties think they are communicating with each other. These attacks can be devastating for the involved parties as all their sensitive information is at risk during the communication.
25. Sinkhole Schemes
A hacker can easily attract all the traffic from a wireless sensor network (WSN) node to build a sinkhole. This type of attack creates a metaphorical sinkhole that compromises the confidentiality of the data and also denies any service to the network. It’s done by dropping all the packets instead of sending them to their destination.
Final Words
IoT is definitely a big deal, and it’s only going to get bigger with the passage of time. Sadly, the bigger it gets, the more targets it has on its back. All the accompanying threats and IoT trends will get bigger as well. Manufacturers and others linked with the IoT industry will have to get serious about the security issues and threats.
Knowledge is the first line of defense against such threats. So, you need to get yourself up to speed with the IoT security threats and their countermeasures.
Related Courses – Learn Online Now
RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
Machine Learning with 9 Practical Applications
Mastering Python – Machine Learning
Data Sciences with Python Machine Learning
Data Sciences Specialization
Diploma in Big Data Analytics
Learn Internet of Things (IoT) Programming
Oracle BI – Create Analyses and Dashboards
Microsoft Power BI with Advance Excel






 WhatsApp Us
WhatsApp Us
Leave a Reply